Question
Experiment 2: Reverse Bias Diode This experiment examines the reverse leakage current in a silicon 1N4004 diode. The reverse current through a PN junction is typically very small (nA), due to the extremely high reverse resistance. This current is called the reverse leakage current. The current is so small that it cannot be measured with a normal DMM. It can only be calculated using Ohm's Law. Note that the diode is now installed in the circuit in reverse bias. The current passing through the diode and the series 470 k resistor will be very small. Since this is a series circuit, the current through the diode will be the same as the current through the resistor. The DMM will measure the very small voltage that develops across the resistor. Since the voltage of the resistor is known, and the value of the resistor is known, the current through the resistor can be calculated. Procedure: 8. Measure the exact value of your resistor. DO NOT TOUCH IT WHILE MEASURING. Enter this measured value in Table 2. TABLE 2 Resistance 1N4004 Use the Agilent meter Vs 30 V R 470 k 9. Build the circuit shown in Figure 5. Figure 5: Reverse Bias Diode 10. Adjust the Current Control setting on the Power Supply to 100 mA. 11. Adjust the voltage of the power supply to each of the Voltages listed in Table 3 and enter the measured Rz voltage for each step in Table 3. 12. Use the measured R2 resistance and measured R2 voltage to calculate the reverse current I for each step and enter your calculated value in Table 3. TABLE 3 Step # Power Supply Voltage 1 0V 2 5V 3 10V 4 20V 5 30V Resistor R Voltage Calculated Current IR
Experiment 2: Reverse Bias Diode
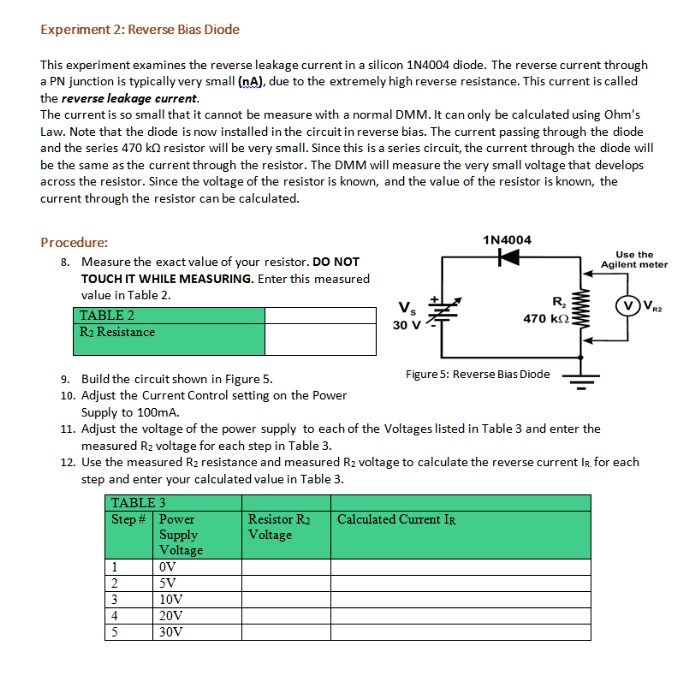
This experiment examines the reverse leakage current in a silicon 1N4004 diode. The reverse current through a PN junction is typically very small (nA), due to the extremely high reverse resistance. This current is called the reverse leakage current. The current is so small that it cannot be measured with a normal DMM. It can only be calculated using Ohm's Law. Note that the diode is now installed in the circuit in reverse bias. The current passing through the diode and the series 470 k resistor will be very small. Since this is a series circuit, the current through the diode will be the same as the current through the resistor. The DMM will measure the very small voltage that develops across the resistor. Since the voltage of the resistor is known, and the value of the resistor is known, the current through the resistor can be calculated.
Procedure:
8. Measure the exact value of your resistor. DO NOT TOUCH IT WHILE MEASURING. Enter this measured value in Table 2.
TABLE 2
Resistance
1N4004
Use the Agilent meter
Vs 30 V
R 470 k
9. Build the circuit shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5: Reverse Bias Diode
10. Adjust the Current Control setting on the Power Supply to 100 mA.
11. Adjust the voltage of the power supply to each of the Voltages listed in Table 3 and enter the measured Rz voltage for each step in Table 3.
12. Use the measured R2 resistance and measured R2 voltage to calculate the reverse current I for each step and enter your calculated value in Table 3.
TABLE 3
Step # Power Supply Voltage 1 0V 2 5V 3 10V 4 20V 5 30V
Resistor R Voltage
Calculated Current IR
Show more…
Added by Kathryn R.
Instant Answer
Step 1
Make sure not to touch the resistor while measuring. Show more…
Show all steps



Gopal Sharma and 65 other
Physics 102 Electricity and Magnetism educators are ready to help you.
Ask a new question