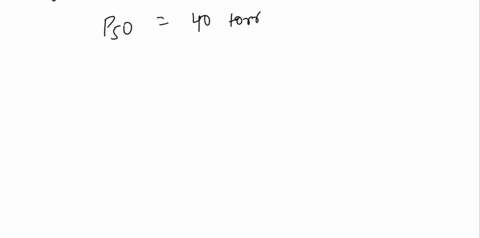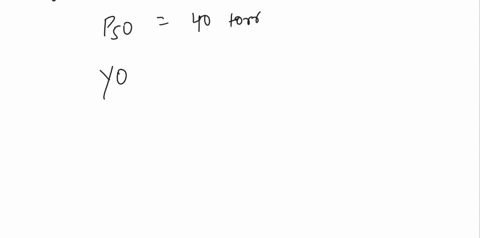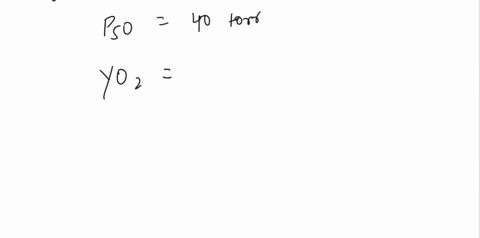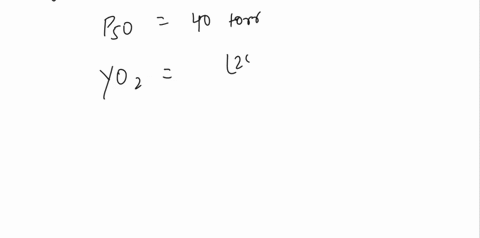Question
Hemoglobin's oxygen binding curve is sigmoidal rather than hyperbolic. The equation for hemoglobin's oxygen binding curve is: Y = (pO2)$^3$/[(P50)$^3$ + (pO2)$^3$] where Y is fractional saturation of hemoglobin. a) Calculate Y when pO2 = 25 torr (a typical venous pO2) and Y when pO2 = 120 torr (a typical oxygen partial pressure in the lungs) given that pCO2 = 5 torr and p50 = 15 torr. b) Calculate Y when pO2 = 25 torr and Y when pO2 = 120 torr given that pCO2 = 80 torr and P50 = 40 torr. c) How much oxygen is delivered to tissues when the pCO2 is 5 torr? How does this compare to the amount of oxygen delivered to tissues when the pCO2 is 80 torr? Express your answers in percentages. d) What role does CO2 play in assisting oxygen delivery to tissues?
Hemoglobin's oxygen binding curve is sigmoidal rather than hyperbolic. The equation for hemoglobin's oxygen binding curve is:
Y = (pO2)$^3$/[(P50)$^3$ + (pO2)$^3$]
where Y is fractional saturation of hemoglobin.
a) Calculate Y when pO2 = 25 torr (a typical venous pO2) and Y when pO2 = 120 torr (a typical oxygen partial pressure in the lungs) given that pCO2 = 5 torr and p50 = 15 torr.
b) Calculate Y when pO2 = 25 torr and Y when pO2 = 120 torr given that pCO2 = 80 torr and P50 = 40 torr.
c) How much oxygen is delivered to tissues when the pCO2 is 5 torr? How does this compare to the amount of oxygen delivered to tissues when the pCO2 is 80 torr? Express your answers in percentages.
d) What role does CO2 play in assisting oxygen delivery to tissues?
Show more…
![Hemoglobin's oxygen binding curve is sigmoidal rather than hyperbolic. The equation for hemoglobin's oxygen binding curve is:
Y = (pO2)^3/[(P50)^3 + (pO2)^3]
where Y is fractional saturation of hemoglobin.
a) Calculate Y when pO2 = 25 torr (a typical venous pO2) and Y when pO2 = 120 torr (a typical oxygen partial pressure in the lungs) given that pCO2 = 5 torr and p50 = 15 torr.
b) Calculate Y when pO2 = 25 torr and Y when pO2 = 120 torr given that pCO2 = 80 torr and P50 = 40 torr.
c) How much oxygen is delivered to tissues when the pCO2 is 5 torr? How does this compare to the amount of oxygen delivered to tissues when the pCO2 is 80 torr? Express your answers in percentages.
d) What role does CO2 play in assisting oxygen delivery to tissues?](https://cdn.numerade.com/ask_images/d8af9817489b43149d6e8001885f9998.jpg)
Added by Rebecca V.
Instant Answer
Step 1
To calculate Y, we can use the equation Y = pO2 / (p50 + pO2). For pO2 = 25 torr: Y = 25 / (15 + 25) = 25 / 40 = 0.625 For pO2 = 120 torr: Y = 120 / (15 + 120) = 120 / 135 = 0.889 Show more…
Show all steps